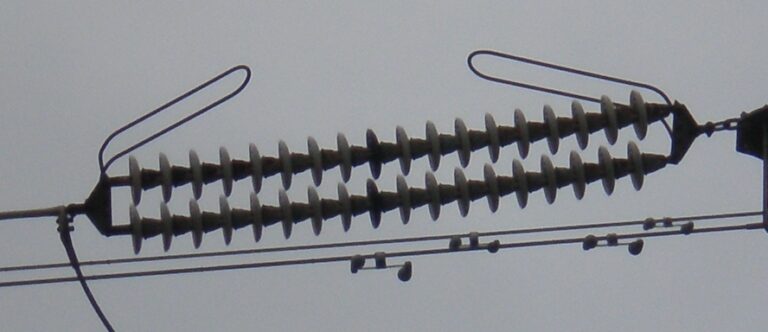
Towers use suspension insulator types due to the pin type insulators’ restrictions for greater voltage. A suspension-type insulator comprises one or more parts linked in series to create a string suspended from the tower’s cross arm or another supporting structure and has a power wire attached to it at its lowest point. An insulator of the string type is another name for this sort of composite unit.
Each suspension insulator disc is built to operate at 11 kV, and the operating voltage rises as more porcelain discs are added to the string and series. For instance, 132 VK transmission lines require 12 insulator discs.
Suspension Insulator
The suspension insulator isolates and electrically supports the line conductors. It comprises many porcelain insulator pieces joined together by flexible metal connections. The bottom of the string is where the conductor is linked. The cost of pin-type insulators would soar if the line’s voltage capacity were increased, rendering them costly and uneconomical to employ. This insulator is thus not cost-effective over 33 kV.
It is customary to use suspension insulator types at higher voltages (>33kv). A series of insulators made up of several porcelain discs is a suspended insulator. Each disc is made to withstand a low voltage of 11 kV. The operating voltage affects the variable disc number in strings. For instance, the string needs three discs when the line voltage is 33 kV.
What function does a suspension insulator serve?
A suspension insulator’s primary job is to hold up the transmission line on the tower, which separates the tower from the transmission line. It is crucial to the reliable flow of power. Depending on the transmission voltage and the consumption situation, suspension insulators are utilized in two or more variants.
Construction and Use of Suspension Insulators
The cross-arms and the insulators, also known as disc insulators, with the number of metallic connections, make up its two primary components. With metallic links, many insulators are connected in series to form a suspension insulator or string.
The bottommost insulator suspends the conductor, and the top end of the insulator is held in place by cross-arms. These insulators are typically utilized in over-headed lines.
Suspension type Insulator
The suspension insulator may be divided primarily into two categories.
- Hewlett or Interlink Type
- Cap and Pin Type
Below is a detailed description of the cap, pin, and Hewlett-type insulator.
• Cap-and-pin type
In a cap-and-pin structure, porcelain is joined by a galvanized cast iron or forged steel cap and a galvanized forged steel pin. The component is connected via clevis-pin connections or ball and socket connectors.
• Interlink Type Insulator
Porcelain is used in the interlink type unit, which has two curving channels with planes at a right angle. These canals functioned as the connecting points for U-shaped leveling coated steel connections. Mechanically speaking, Interlink type insulators are more robust than cad-and-pin units.
If the porcelain between the links cracks, the metallic link still holds the lineup. The supply is not cut off as a result. Electrical strain is applied substantially on the porcelain in a Hewlett-type insulator between the linkages. Therefore this is its main drawback. As a result, its puncture stress is lower than other types.
Read More: What Is Sub Soil Drainage? Its Advantages and Other Interesting Facts Revealed
Advantages of suspension insulators
When the operating voltage exceeds 50kV, suspension insulators are less expensive than pin-type insulators. Each suspension insulator (insulator disc) unit is made for a relatively low voltage (11kV), and by joining these modules in series, the insulation strength may be increased. Depending on the operating voltage, insulator discs must be used in a certain quantity.
In this suspension-type insulator configuration, mechanical loads brought on by the wind and other causes are decreased, while suspension-type insulators provide the line more flexibility. Thanks to the connection at the cross arm, the insulator string is free to swing in any direction and enter a position where it only experiences tensile stress.
The advantage of using suspension-type insulators in conjunction with steel supporting structures is that it lessens the conductor’s susceptibility to cross-arm effects, allowing the tower to serve as a lightning rod.
If the load on the transmission line increases quickly, increasing the line voltage rather than adding more conductors can meet the increased demand. Additional line insulation requirements for suspension-type insulators can be met by simply attaching one or more discs to the string.
Disadvantages
As each gadget has drawbacks of its own, it is preferable to list a few shortcomings of the suspension type insulator:
The suspension insulator string is more costly than the pin and post insulator. Higher voltage lines, however, are more cost-effective. Unlike pin or post insulators, suspension insulators require a taller supporting structure.
The current conductors’ ground clearance is maintained by using this taller structure. The conductors’ accessible swing amplitude is more significant in suspension insulator systems. Therefore, a wider gap between conductors should be taken into account.
Apart from this, if you are interested to know more about Denmark Cost Of Living then visit our BUSINESS category.